Nasr City, 52 El Tayaran Street, in front of the Health Insurance Hospital

Treatment of benign brain tumors
Brain tumors are a scary thought for many individuals as they can severely impact one's quality of life. However, not all brain tumors are cancerous or malignant. In fact, there are many cases where brain tumors may be benign, meaning that they are non-cancerous and can be easily treated with the right approach. Nevertheless, it is essential to understand the treatment options available when dealing with such conditions. In this blog, we will delve into the various treatments available for benign brain tumors and how they can help individuals get back to their normal life. So, let's dive in!
Introduction to Benign Brain Tumors
Benign brain tumors, also known as noncancerous brain tumors, are abnormal growths of cells in the brain that do not contain cancer cells. These tumors are different from their malignant counterparts in that they have clear borders, meaning they do not invade surrounding tissue. Although they are not cancerous, benign brain tumors can still be serious and life-threatening. However, many of these tumors can be successfully treated. Surgery is often the primary treatment for benign brain tumors and can usually remove the entire tumor. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy may also be used as part of a combination treatment approach. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for successful treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of life-threatening complications. In the following sections, we will discuss treatments for benign brain tumors in more detail, including the types of cells that cause these tumors and the differences between benign and malignant brain tumors.
Surgery as a Primary Treatment for Benign Brain Tumors
When it comes to treating benign brain tumors, surgery is the primary treatment option. This involves the removal of the tumor through an incision in the skull. The success of the surgery depends on the size, location, and type of tumor. In many cases, complete removal of the tumor is possible, leading to a positive outcome. However, surgery also carries risks, such as bleeding, infection, and damage to healthy brain tissue. Therefore, a skilled and experienced neurosurgeon is essential to ensure the best possible outcome. Additionally, follow-up care is necessary to monitor the patient's recovery and prevent recurrence of the tumor. In the next sections of the blog, we will explore other treatment options and discuss the importance of early diagnosis and treatment for benign brain tumors.
Radiation Therapy for Benign Brain Tumors
Radiation therapy is another option for the treatment of benign brain tumors. This therapy uses high-energy radiation to shrink or destroy tumor cells. Like surgery, it is a local treatment, but instead of physically removing the tumor, it uses X-rays or other types of radiation to kill the tumor cells. This type of therapy can be done externally or through an implanted device. The GliaSite radiation therapy system is a newer, more targeted radiation therapy that has shown promise in the treatment of certain types of benign brain tumors. It's important to note that while radiation therapy can be effective, it does carry some risks, so it's essential to thoroughly discuss the benefits and potential side effects with your doctor before choosing this treatment option. In some cases, radiation therapy may be used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy to provide the best possible outcomes for patients with benign brain tumors.
Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Benign Brain Tumors
Chemotherapy is a treatment option for both cancerous and non-cancerous brain tumors. For benign brain tumors, chemotherapy may be used on its own, or in combination with other treatments, such as radiation therapy or surgery. Chemotherapy works by targeting rapidly dividing cells in the body and stopping or slowing their growth. It can be taken orally or through an IV, and in some cases, may involve the placement of medication directly into the tumor. The use of chemotherapy in the treatment of benign brain tumors may depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the general health of the patient. While chemotherapy can be effective in controlling the growth of benign brain tumors, it may also cause side effects, such as nausea and hair loss. As with any treatment, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks before making a decision.
Combination Treatments for Benign Brain Tumors
Combination treatments for benign brain tumors are often used to achieve a more effective outcome. Surgery is typically the primary mode of treatment for benign brain tumors, but combination treatments can include chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that works to kill rapidly dividing cells, while radiation therapy is a local treatment that targets cells in the specific area of treatment. Combination therapy may involve using lower doses of chemotherapy and radiation therapy in conjunction with surgery. This can help reduce the chances of tumor recurrence and improve survival rates. Patients with benign brain tumors may require follow-up treatment to monitor for recurrence and ensure the tumor has been fully removed. Combining treatments can be a highly effective strategy, guided by a patient's medical history and individual circumstances.
Follow-up Care for Benign Brain Tumors
After being treated for a benign brain tumor, it is important to continue follow-up care to monitor for any recurrence or new neurological symptoms. The follow-up schedule will usually be determined by your healthcare provider but may include regular imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans. For some patients, additional treatment such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be necessary. It is also important to maintain overall good health and seek medical attention if any new symptoms arise. Early detection and treatment of any recurrence or new tumors is essential for the best possible outcomes. By working closely with your healthcare providers and following a comprehensive follow-up care plan, patients with benign brain tumors can achieve long-term tumor control and optimal quality of life.
Types of Cells that Cause Benign Brain Tumors
When it comes to the types of cells that cause benign brain tumors, there are several possibilities. Meningiomas are one of the most common types, arising from the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Schwannomas, as mentioned earlier, are another frequent culprit, originating from the cells that wrap around and insulate nerves. Other types of benign brain tumors can arise from cells such as astrocytes, ependymal cells, and pituitary gland cells. While it's important to know the specific type of tumor you have in order to determine the best treatment plan, what matters most is receiving prompt and effective care. Whether you end up undergoing surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or some combination thereof, the goal is always to shrink or remove the tumor and prevent further growth or recurrence. By keeping up with follow-up care and making lifestyle changes as necessary, you can enjoy a healthy, happy life post-tumor.
Differences between Benign and Malignant Brain Tumors
It's important to understand the differences between benign and malignant brain tumors in order to properly treat them. Malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body, while benign tumors are non-cancerous and usually easier to treat. Benign tumors grow slowly and have distinct boundaries, while malignant tumors often grow rapidly and can invade surrounding tissues. Treatment options for benign tumors typically include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these treatments. Early diagnosis and treatment is crucial for both types of tumors, but the life-threatening risks associated with untreated malignant tumors are much greater than those of untreated benign tumors. By understanding these differences, doctors can develop a treatment plan that provides the best outcomes for their patients.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment for Benign Brain Tumors
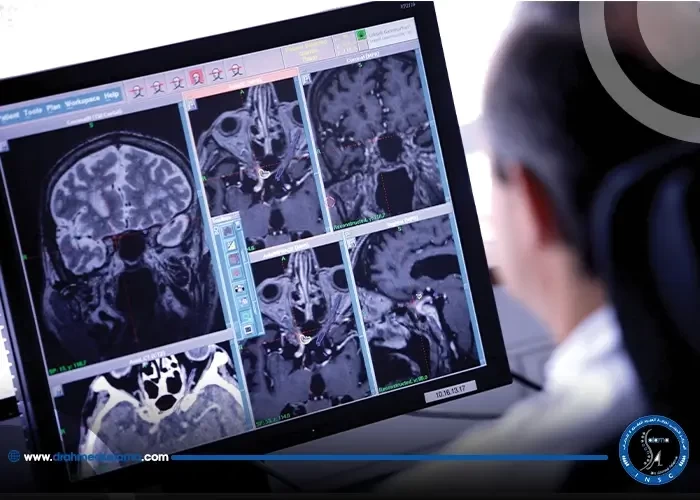
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for successfully managing benign brain tumors. As with most medical conditions, early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and a full recovery. In the case of benign brain tumors, delaying treatment can lead to serious complications and even life-threatening risks. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the symptoms of a brain tumor and seek medical attention immediately if there are any concerns. Proper diagnostic procedures, such as imaging tests and biopsies, can help determine the exact location and size of the tumor. Once diagnosed, a treatment plan can be developed including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these options. Regular follow-up care is also essential to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and prevent any potential recurrence. Bottom line, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful management of benign brain tumors, prevent complications and mitigate the risks of life-threatening outcomes.
Life-threatening Risks of Untreated Benign Brain Tumors.
The consequences of leaving a benign brain tumor untreated can be life-threatening. As the tumor grows, it can compress vital structures of the brain, causing severe neurological deficits or even death. Benign brain tumors can also increase intracranial pressure, leading to headaches, vision changes, and seizures. Delayed diagnosis of a benign brain tumor can also result in the tumor growing to a size that makes complete removal impossible, or even cause the tumor to convert into a malignant one over time. It is crucial to seek medical attention at the first sign of symptoms to avoid life-threatening risks associated with untreated benign brain tumors. Through early diagnosis and prompt treatment, individuals with benign brain tumors can have a successful recovery and a better quality of life.
Is a benign brain tumor dangerous?
Brain tumors are inherently dangerous, but benign tumors are non-cancerous cells that do not spread to other parts of the body and usually do not recur after removal. They do not pose a risk to the brain unless left untreated.
Can a patient with benign brain cancer be cured?
Yes, a patient with benign brain cancer can be cured through surgical removal, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and other methods that eliminate benign brain tumors.