Nasr City, 52 El Tayaran Street, in front of the Health Insurance Hospital

brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure

Did you know that high blood pressure can be a major cause of brain hemorrhages? Some people may think that this type of hemorrhage only occurs due to physical injuries, but the truth is that chronic high blood pressure is one of the most significant factors that puts the blood vessels in the brain at risk. When blood pressure is consistently high, blood vessels can be damaged, leading to rupture and brain hemorrhage. In this article, we will discuss how brain hemorrhages due to high blood pressure occur, the importance of monitoring blood pressure to prevent this dangerous condition, and whether brain hemorrhages can be treated.
Brain Hemorrhages Due to High Blood Pressure
Brain hemorrhages due to high blood pressure are one of the most serious complications of uncontrolled blood pressure. The rupture of tiny blood vessels within the brain causes blood to leak into the surrounding tissue, destroying nerve cells and putting pressure on vital brain centers. The danger of this type of hemorrhage lies in its rapid progression and the potential for immediate life-threatening complications, which prompts some to ask: Can brain hemorrhages cause death?
The answer depends on several factors, including the speed of diagnosis, the location of the hemorrhage, and the extent of damage to brain tissue. However, prompt medical intervention can make a significant difference in survival rates.
In this context, treatment options for a hypertensive brain hemorrhage vary, ranging from controlling blood pressure to delicate surgical procedures aimed at reducing intracranial pressure and preventing further damage. This is where the specialist physician makes the most appropriate decision for the patient's condition, based on the extent of the hemorrhage, the state of consciousness, and brain function.
If you are experiencing some of the symptoms of a hypertensive brain hemorrhage or would like an accurate diagnosis, do not hesitate to contact Dr. Ahmed Salama. His specialized medical team will provide you with the optimal treatment and the most effective approach to help you recover quickly. Call now to schedule an appointment and benefit from accurate and comprehensive medical consultations.
Hypertensive Brain Hemorrhage: Learn the Risks, Symptoms, and Prevention
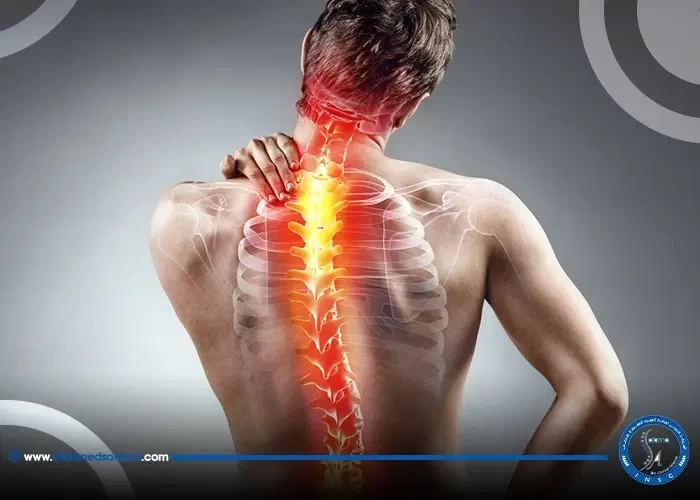
Hypertensive brain hemorrhage is one of the most serious health complications that can be life-threatening without warning. Uncontrolled high blood pressure places severe pressure on the blood vessels in the brain, which can lead to rupture and internal bleeding, causing direct damage to brain tissue. Symptoms of this hemorrhage may appear suddenly and include severe headache, weakness, difficulty speaking, and loss of consciousness. Early prevention by controlling blood pressure and adopting a healthy lifestyle is the best defense against this serious condition. Learn in this article about the most important signs of a brain hemorrhage associated with high blood pressure, and how to deal with them quickly to avoid serious complications that could lead to death or permanent disability.
6 of the most common risks of spinal surgeries. Learn about them.
Brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure
Brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure is a serious medical condition that can lead to significant damage to brain tissue. When blood pressure is chronically high, the inner walls of the blood vessels in the brain become weak and vulnerable to damage. If the high pressure persists, these vessels may become damaged and blood may leak into the surrounding tissue, leading to internal bleeding. This condition is known as a hypertensive brain hemorrhage, and it is one of the leading causes of this health problem in adults.
What is the success rate of spinal surgeries?
Symptoms and contributing factors of hemorrhage
The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure vary depending on the size of the hemorrhage and its location. Common symptoms include a sudden, severe headache, weakness in the extremities, difficulty speaking, or loss of balance. Patients may also experience changes in their level of consciousness or even faint in severe cases. Other factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, or a family history of heart disease or high blood pressure, increase the risk of a brain hemorrhage. People who do not take the necessary medications to control their high blood pressure are also at greater risk.
Treatment for kyphosis after age 18
Prevention and Treatment
To prevent brain hemorrhages due to high blood pressure, it is essential to monitor blood pressure levels regularly and follow a healthy lifestyle. This includes taking prescribed blood pressure-lowering medications, stopping smoking, and reducing salt and alcohol consumption. If a hemorrhage occurs, treatment may require immediate medical intervention, such as medications to reduce intracerebral pressure or surgery to remove the accumulated blood. In addition to medical treatment, the patient is monitored in the intensive care unit to ensure their condition is stabilized and reduce future risks.
Types of Brain Hemorrhages
Brain hemorrhages due to high blood pressure occur in several forms, varying depending on the location of the hemorrhage, which affects the diagnosis and treatment of the brain hemorrhage.
Brain hemorrhages due to high blood pressure include:
Intracerebral hemorrhage: This occurs within the brain tissue and is considered one of the most serious types of brain hemorrhage.
Intraventricular hemorrhage: This occurs within the cavities of the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: This type of hemorrhage occurs in the space between the brain and the membranes covering it, and is often caused by a ruptured artery.
Subdural hemorrhage: This type occurs when blood collects between the brain and the membranes surrounding it, and is usually associated with head injuries.
Epidural hemorrhage: This type of hemorrhage occurs between the skull and the outer membrane of the brain, and is often the result of a direct injury or blow to the head.
In some simple cases, such as treating a blood spot in the brain, close medical observation and follow-up may be sufficient without surgical intervention.
Cost of Scoliosis Surgery in Egypt
Symptoms of a Brain Hemorrhage
The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage caused by high blood pressure vary depending on the size and location of the hemorrhage within the brain. Symptoms may range from mild to severe, and in some cases, they may appear suddenly and require immediate medical intervention. Symptoms of a mild brain hemorrhage include:
Sudden severe headache: This is the most common symptom and is felt suddenly and severely.
Weakness or numbness on one side of the body: The patient may experience sudden weakness or numbness in an arm, leg, or even an entire side of the body.
Difficulty speaking or understanding words: The patient may have difficulty speaking or understanding words normally.
Nausea and vomiting: The patient may experience nausea and vomiting for no apparent reason.
Dizziness and loss of balance: Some people experience dizziness and loss of balance.
Vision problems: Such as sudden double vision or blurred vision.
Change in level of consciousness: A sudden change in level of consciousness may occur, such as extreme drowsiness or partial loss of consciousness.
As for when symptoms of internal bleeding in the head begin, they may appear suddenly, usually within minutes to hours of the onset of bleeding. They must be treated quickly to reduce potential risks.
If you suffer from high blood pressure, learn about ways to prevent a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure before it's too late.
Treatment of a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure
Treatment of a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure depends on several factors, most notably the location and severity of the hemorrhage, as well as the patient's health condition. The treatment plan aims to control the bleeding, minimize damage to the brain, and support vital functions. The following are the most common types of treatment used:
Drug Therapy
Used in cases that do not require surgical intervention, it aims to control symptoms and reduce intracranial pressure:
Medications to control high blood pressure.
Anticonvulsants to prevent seizures.
Pain relievers and sedatives to reduce nervous tension.
Medications to reduce brain swelling, such as cortisone.
Laxatives to avoid straining during defecation, thus reducing intracranial pressure.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment is one of the primary options for life-threatening brain hemorrhages caused by high blood pressure or those that cause serious neurological complications. The type of surgery depends on the location and size of the hemorrhage, and its impact on brain function. Here are the most common surgical treatment methods:
Removing a portion of the skull bone (craniectomy) to relieve pressure on the brain.
Surgical drainage of the blood clot or catheter drainage in the presence of a large hemorrhage.
Inserting a catheter to drain cerebrospinal fluid in the presence of hydrocephalus or increased intracranial pressure.
Intensive Care and Vital Support
This is essential to ensuring the patient's stability and avoiding sudden complications:
Close monitoring in the intensive care unit to monitor vital signs.
Use of mechanical ventilation if necessary.
Providing fluids and nutrition via an intravenous or feeding tube.
Rehabilitation after treatment
The rehabilitation phase begins after the patient's condition has stabilized, with the goal of restoring brain function and improving quality of life:
Physical, occupational, and speech therapy sessions.
Continuous neurological monitoring to prevent recurrence of bleeding.
A rapid response to treatment plays a pivotal role in reducing the risk of complications and increasing the chances of recovery, but the most important question remains: Can a brain hemorrhage be cured? The answer to this question depends on the timing of medical intervention and the severity of the hemorrhage, as every critical moment can significantly impact the chances of recovery.
Discover the steps for early diagnosis of a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure and begin safe treatment with a trusted specialist.
What is the survival rate for a brain hemorrhage?
The survival rate for a brain hemorrhage varies greatly depending on several factors, including the size of the hemorrhage, its location, and the timing of treatment. In cases of hypertensive brain hemorrhage, studies indicate that the survival rate is higher with prompt medical intervention. If treatment is early and effective, the survival rate can reach approximately 50% or more, especially if the injury is less severe.
For survivors of a brain hemorrhage, recovery may be lengthy, especially if the injury is large or in sensitive areas of the brain. However, prompt intervention and treatment of a hypertensive brain hemorrhage can significantly improve the outcome.
However, the survival rate may also be affected by other health factors, such as age and the presence of other conditions such as diabetes or heart disease, and therefore varies from person to person.
How long does it take to recover from a brain hemorrhage?
The recovery time for a brain hemorrhage varies depending on the severity of the injury, the location of the hemorrhage, and the timing of medical intervention. In mild cases, the patient may need between 3 and 6 months to recover, while in more severe cases, recovery may take from 6 months to a year or more. Recovery also depends on the patient's general health and age, as well as the importance of rehabilitation therapy, including physical and occupational therapy. Therefore, it is important to follow up with a specialized medical team to ensure optimal results and minimize any future complications.
Don't neglect the symptoms of a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure. Book your consultation now with Dr. Ahmed Ibrahim Salama.
When is the risk of a brain hemorrhage over?
In cases of a brain hemorrhage due to high blood pressure, the first week after the injury is the most dangerous period, as the patient is susceptible to complications such as worsening of the hemorrhage or increased intracranial pressure. However, as time passes and the condition stabilizes, the risk gradually decreases, especially with rapid response to treatment and access to intensive care.
However, the answer to the question "Can a brain hemorrhage be cured?" depends on several factors, most notably the severity of the hemorrhage, its location within the brain, and the extent of damage to the nerve cells. While severely damaged brain tissue cannot be restored, other areas of the brain can regain some function through intensive rehabilitation.
Treatment programs for hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage, which include drug therapy and neurorehabilitation, are essential in accelerating the recovery period, which can last from several months to more than a year. With the patient's commitment to treatment and rehabilitation, they may gradually return to their daily activities, meaning the risk subsides gradually rather than immediately.
Why is Dr. Ahmed Ibrahim Salama recommended?
In critical cases such as hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage, it is essential to rely on a doctor with experience, skill, and accurate decision-making. Dr. Ahmed Ibrahim Salama is a distinguished physician in this specialty for the following reasons:
Extensive experience in neurosurgery and spinal surgery.
Highly accurate diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhage and immediate management.
Using the latest surgical techniques and advanced endoscopies.
Personal attention to follow-up before and after surgery.
A proven track record of success in treating critical and complex cases.
In conclusion, hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage is one of the most serious neurological conditions that requires rapid medical intervention. The timing of treatment and the skill of the physician directly impact the recovery rate and minimize complications. Although some patients may face long challenges during the recovery period, early diagnosis, a comprehensive treatment plan, and appropriate rehabilitation open the door to hope for many survivors of hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. If you are looking for specialized care and effective treatment for cerebral hemorrhage cases, Dr. Ahmed Ibrahim Salama, a consultant neurosurgeon, is a trustworthy choice, thanks to his extensive experience and successful outcomes in treating hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage.
Does the patient survive a brain hemorrhage?
Yes, many patients survive a brain hemorrhage, especially when they receive prompt treatment and intensive care. Recovery depends on the size and location of the hemorrhage and the speed of medical intervention. However, in severe cases or when treatment is delayed, the hemorrhage can lead to serious complications.
Can a brain hemorrhage recur?
Yes, recurrent bleeding in the brain is possible, especially if causative factors such as high blood pressure or vascular disorders are not controlled.
When does the danger pass for a patient with a brain hemorrhage?
Recovery after a brain hemorrhage may vary depending on the area of the brain affected and the severity of the impact. In mild paralysis, recovery is usually observed within 3–6 months. However, fine hand movements, known as fine motor skills, may take a little longer to recover.
When is a brain hemorrhage fatal?
A brain hemorrhage can be life-threatening and cause permanent brain damage. The severity and outcome of a brain hemorrhage depend on its cause, location within the skull, the size of the hemorrhage, and the amount of time between the hemorrhage and treatment. Once brain cells die, they do not regenerate, and the damage can be severe, leading to physical, mental, and functional impairment.